The United Arab Emirates is moving fast toward a fully digital tax environment. With a Peppol-based e-invoicing network, real-time data reporting and a phased mandate, the UAE’s e-Invoicing Programme will soon change how every business issues and receives invoices.
This guide walks through what e-Invoicing means in the UAE, who is in scope, the official deadlines, key requirements and how your business can prepare.
What is e-Invoicing in the UAE?
In the UAE, an electronic invoice (e-invoice) is a structured, machine-readable tax document that can be processed automatically by the systems of the seller, buyer and the tax authority.
The UAE e-Invoicing Programme is built around:
- A Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control and Exchange (DCTCE) “5-corner” model, where invoices flow through Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) over the Peppol network, while key tax data is reported to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) in near real time.
- A standard data model called PINT AE, which defines the mandatory and optional fields for UAE e-invoices, tax credit notes and related documents.
This architecture is designed to improve VAT compliance, transparency, and auditability.
What is B2B e-Invoicing in the UAE?
B2B e-invoicing covers structured electronic invoices exchanged between businesses for domestic supplies in the UAE and eligible cross-border transactions where a UAE tax invoice is required under the VAT rules.
Applies to most business-to-business transactions, including supplies between mainland entities, free zone entities (where in scope) and non-resident businesses with UAE-taxable transactions, unless a specific exclusion applies.
What is B2G e-Invoicing in the UAE?
B2G e-invoicing refers to electronic invoices issued by businesses to UAE federal government entities and potentially certain other public bodies.
The UAE framework makes B2G transactions a core part of the mandate. Government entities themselves must appoint an ASP and be ready to receive e-invoices before the B2G go-live date.
What is B2C e-Invoicing in the UAE?
For now, B2C transactions, sales to end consumers, are out of scope of the UAE’s national e-invoicing mandate. The current framework and Ministerial Decisions explicitly focus on B2B and B2G transactions; B2C is excluded at this stage.
The Ministry of Finance may extend the framework to B2C via a separate decision in the future, but no such move has been formally announced yet.
Retailers and service providers can continue to issue traditional receipts to consumers for now, but adopting digital formats voluntarily is also possible.
Is e-Invoicing mandatory in the UAE?
In the UAE, e-invoicing is becoming mandatory through a phased rollout.
Legally, the foundations were laid when Federal Decree-Law No. 16 of 2024 amended the VAT Law to formally recognise electronic invoices as valid tax documents from 30 October 2024.
The detailed rules and go-live dates are then set out in Ministerial Decisions No. 243 and 244 of 2025, along with updates to the VAT Executive Regulations.
In practice:
- The e-invoicing system becomes operational in July 2026 (pilot and voluntary phase).
- Mandatory e-invoicing is phased in from 2027, based on turnover thresholds and taxpayer type.
e-Invoicing Deadlines in the UAE
The UAE has opted for a phased rollout to give businesses time to adapt. The dates below reflect the latest public information from tax advisors and solution providers summarising Ministerial Decisions 243 and 244 of 2025:
Key milestones:
- Q4 2024 – Q2 2025
- E-invoicing legislation and technical documentation released; service provider accreditation opens.
- February 2025
- Public Consultation Document and PINT AE Data Dictionary published.
- 1 July 2026
- Pilot programme starts (Taxpayer Working Group).
- Voluntary participation for other businesses; early adopters can test integrations and processes in a live environment.
- 31 July 2026
- Large taxpayers (annual revenue ≥ AED 50 million) must have appointed an Accredited Service Provider.
- 1 January 2027 – Phase 1 (Large taxpayers)
- Mandatory e-invoicing for B2B transactions for businesses with annual revenue ≥ AED 50 million.
- 31 March 2027
- Small and medium businesses and government entities must have appointed an ASP.
- 1 July 2027 – Phase 2 (Other taxpayers)
- Mandatory e-invoicing for all remaining in-scope businesses (revenue < AED 50 million).
- 1 October 2027 – B2G go-live
- Government entities must receive (and in some cases issue) e-invoices via the national system; B2G transactions are fully digital.
Because future decisions may refine dates or thresholds, businesses should monitor MoF and FTA communications continuously.
Who is obliged to use e-Invoicing in the UAE?
E-invoicing requirements apply not only to taxable persons, but to all businesses operating in the UAE, regardless of their VAT registration status, for in-scope transactions.
In broad terms, the mandate covers:
- All businesses (mainland and free zone) issuing in-scope B2B and B2G invoices in the UAE.
- VAT-registered entities and, where applicable, non-VAT-registered businesses engaged in taxable business transactions.
- Non-resident businesses that have taxable supplies in the UAE and must issue UAE-compliant tax invoices.
Some sectors and transaction types are expressly excluded but the default assumption is that business transactions are in scope unless an exclusion applies.
How to generate e-Invoices in the UAE?
From an implementation perspective, generating compliant e-invoices in the UAE generally involves five steps:
- Appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP)
- You must use a MoF-accredited ASP from the official list published by the Ministry of Finance.
- Prepare your ERP and data
- Map your invoice data to the PINT AE Data Dictionary, which includes mandatory and conditional fields for different use cases.
- Create the e-invoice in structured format
- Your ERP or billing system generates invoice data, which is sent to your ASP.
- The ASP validates the data and converts it into the UAE standard XML format (PINT AE XML), if it is not already in that form.
- Exchange and reporting
- The ASP sends the invoice via the Peppol 5-corner network to the buyer’s ASP, and both ASPs report the relevant Tax Data Document (TDD) to the FTA’s central platform.
- Message-level status (MLS) responses confirm whether the invoice and tax data have been successfully exchanged and reported.
- Archive and monitor
- E-invoice data must be stored within the UAE (or otherwise in line with the Tax Procedures Law) and made available to the FTA on request.
- Depending on the applicable UAE tax rules, e- invoices must be archived in line with the general record-keeping periods – typically at least 5-years for VAT purposes and at least 7-years where UAE Corporate Tax applies, with longer periods in specific cases.
- System failures must be reported within two business days.
United Arab Emirates e-Invoicing Requirements
For an invoice to qualify as an e-invoice in the UAE, it must first meet all tax invoice requirements under UAE VAT law. This includes accurate supplier and customer details, a clear description of the goods or services supplied, applicable VAT rates, VAT amounts and the total amount due.
In addition to this, a UAE e-invoice must:
- Be issued in a structured, machine-readable format, using the UAE PINT AE XML data model.
- Contain all mandatory PINT AE data elements, such as document identifiers, supply and invoice dates, currency, tax category codes, VAT breakdowns and totals, in line with the national specifications.
- Be created and exchanged via a UAE ASP connected to the Peppol network, ensuring that the invoice can be validated, delivered to the buyer and reported to the FTA.
- Be issued within the required time limits (e.g. within 14 days of the taxable transaction) and retained in accordance with the UAE Tax Procedures Law, with data stored in the UAE and available to the FTA on request.
Only invoices that satisfy both the content requirements of a UAE tax invoice and the technical standards of PINT AE, and that are routed through an accredited ASP, are treated as compliant e-invoices under the UAE e-invoicing regime.
What are the Benefits of e-Invoicing for Businesses in the UAE?
Beyond pure compliance, the UAE’s e-invoicing framework is intended to create value for both businesses and the wider economy by speeding up invoicing and payments, reducing manual processing and errors, improving the consistency of VAT documentation, and enhancing overall transparency. Over time, this should support better use of transaction data for oversight and contribute to a gradual shift toward a more digital, paper-light business environment.
The UAE Data Dictionary (PINT AE)
A fundamental component of the UAE’s e-Invoicing system is the PINT AE Data Dictionary, which defines the mandatory and optional data elements for invoices. This structured format ensures consistency, accuracy, and compliance across different industries and ERP systems.
Key Components of PINT AE
- Invoice Identification – Each invoice must have a unique invoice number and issue date.
- Supplier and Buyer Details – Including tax identification numbers and business registration details.
- Transaction Classification – Identification of reverse charge transactions, margin schemes, and exports.
- VAT Calculation Fields – Pre-defined tax rates, exemptions, and taxable amounts.
- Structured XML Format – Ensuring invoices are machine-readable and compatible with the FTA’s system.
The PINT AE framework ensures that all invoices exchanged follow a standardized format, reducing the risk of errors and simplifying tax audits.
Typical use cases using the Data Dictionary
The UAE’s e-Invoicing system identifies 16 different invoicing scenarios, each with specific compliance requirements. Businesses must ensure that their invoicing practices align with these scenarios.
| Use case | Description | Details |
| 1 | UAE Standard tax invoice | Mandatory and commonly used optional fields |
| 2 | Supply under Reverse charge | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 3 | Mechanism | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 4 | Zero rated supplies | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 5 | Deemed supply | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 6 | Disclosed agent billing | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 7 | Summary tax invoice | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 8 | Continuous supplies | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 9 | Supply involving free trade zone | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 10 | Supply through e-commerce | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 11 | Exports | Additional requirements beyond use case 1 |
| 12 | Margin scheme | Mandatory and commonly used optional fields |
| 13 | Standard tax credit note | Additional requirements beyond use case 12 |
| 14 | Disclosed agent billing tax credit note | Mandatory and commonly used optional fields |
| 15 | Commercial Invoice | Mandatory and commonly used optional fields |
| 17 | Self-billing | Mandatory and commonly used optional fields |
Each scenario has unique data fields and validation steps, requiring businesses to ensure their invoices are properly categorized to avoid rejection.
The PEPPOL 5-Corner Model
The UAE has adopted a PEPPOL-based 5-Corner Model, an internationally recognized framework for structured invoice exchange. This model establishes a standardized communication network for suppliers, buyers, service providers, and tax authorities.
The invoice exchange process follows these steps:
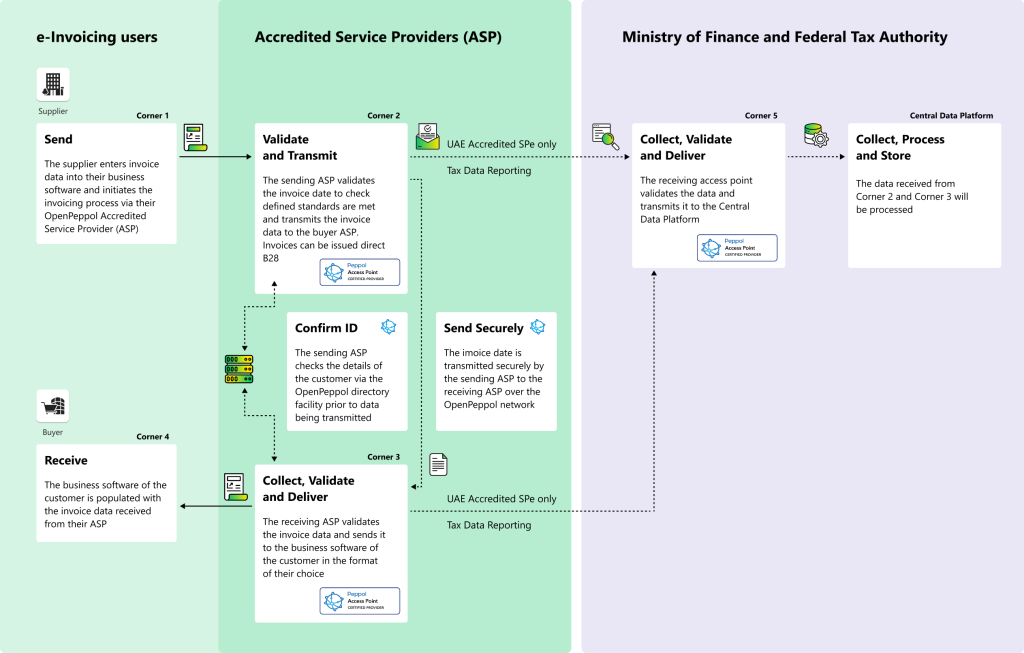
- Supplier (Corner 1) submits eInvoice data (PINT AE) in an agreed format with its UAE Accredited Service Provider (Corner 2)
- C2 validates the eInvoice data received from C1 and converts it into the UAE standard eInvoice xml format (if C2 has received the eInvoice in a different format from C1).
- C2 transmits the eInvoice (in the xml format) to the Buyer’s UAE accredited Service Provider (Corner 3)
- In parallel, C2 reports the Tax Data Document (TDD) to Corner 5
- Upon validating the eInvoice, C3 sends a Message Level Status (MLS) to C2
- C3 submits the eInvoice to the Buyer (Corner 4) in an agreed format with its UAE Accredited Service Provider (Corner 3)
- Upon successful validation of the eInvoice, C3 also reports the Tax Data Document (TDD) to Corner 5. If the validation of the eInvoice was unsuccessful, C3 reports a negative MLS to C2 as well as to C5. In this scenario, there will be no reporting of the TDD to C5 by C3
- C5 sends a Message Level Status (MLS) to C2 once the TDD has been successfully reported
- C5 sends a Message Level Status (MLS) to C3 once the TDD has been successfully reported
- C2 forwards the C3 exchange MLS and C5 reporting MLS to C1.
- C3 forwards the C5 reporting MLS to C4.
FAQs about e-Invoicing in the UAE
What is the standard format for e-Invoices in the UAE?
The UAE has chosen PINT AE (the UAE version of Peppol International invoicing) as its core data model.
In practice, this means:
- Invoices are exchanged in XML using PINT AE format, with clearly defined business terms and validation rules.
- Around 50 mandatory data elements, plus many conditional/optional fields, must be populated depending on the use case (standard invoice, self-billing, summary invoices, exports, margin scheme, etc.).
- ASPs may accept other syntaxes (such as UBL 2.1 or JSON) from your ERP, but they must convert them to the UAE standard XML before transmitting and reporting.
Can small businesses benefit from e-Invoicing in the UAE?
From 1 July 2027, e-Invoicing in the UAE becomes mandatory for all remaining in-scope businesses with annual revenue below AED 50 million (i.e. most small and medium-sized enterprises that were not already covered in the first phase for large taxpayers from 1 January 2027). In practice, this means that SMEs operating in the UAE and issuing B2B or B2G invoices will need to connect their accounting or ERP systems to a UAE-accredited Service Provider, issue invoices in the PINT AE XML format, and ensure those invoices are exchanged and reported. While this adds a new compliance requirement, it can also help smaller businesses speed up invoicing and collections, reduce manual errors and VAT issues, and gradually move away from paper-based processes to more efficient, digital finance operations.
Are there any exemptions to the e-Invoicing requirements in the UAE?
Ministerial Decision 243 of 2025 and related guidance outline exclusions for certain categories of transactions, for example:
- Specific government activities in a sovereign capacity,
- Certain airline passenger and cargo transport services,
- Some exempt or zero-rated financial services,
- Other categories that the Minister of Finance may designate over time.
In addition, B2C retail transactions are out of scope for the national mandate at this stage.
Are there penalties for non-compliance with e-Invoicing regulations in the UAE?
Non-compliance with the UAE e-invoicing rules is penalised under the general administrative penalty regime for tax violations (Cabinet Decision No. 40 of 2017, as amended by Cabinet Decisions No. 49 of 2021 and No. 129 of 2025). From 14 April 2026, the main penalties relevant to e-invoicing include:
• Failure to issue a tax invoice / e-invoice, tax credit notes or equivalent document within the legally specified period (e.g. the 14-day deadline) – AED 2,500 per detected case.
• Failure to keep the required tax records and e-invoicing data – AED 10,000 per violation, increasing to AED 20,000 for repeated violations within 24 months.
Additional penalties may apply for late payment of tax, incorrect returns or other breaches.
What software solutions are available for e-Invoicing in the UAE?
In practice, e-invoicing compliance in the UAE revolves around working with a UAE-accredited Service Provider (ASP). ASPs act as the technical bridge between your ERP or accounting system and the national e-invoicing infrastructure: they validate invoice data against the UAE PINT AE specifications, convert it into the required XML format, exchange e-invoices over the Peppol network, and report the relevant tax data to the FTA.
Businesses can either use an ASP’s own platform directly or connect their existing finance systems to an ASP via standard integrations or APIs. Additionally, businesses can verify accredited service providers and their technical capabilities through listings available in the Peppol Directory.
RTC Suite is a cloud-based e-Invoicing and tax compliance platform on SAP BTP that connects seamlessly with all ERPs, billing systems, and IoT devices, and is continuously updated for the latest regulatory requirements. A recognised SAP Partner as well as a member of PEPPOL and GENA, RTC already operates as a Peppol Access Point and is in the process of obtaining ASP accreditation for UAE e-invoicing. Dariba Tech is our authorised partner in the UAE and across the wider GCC region, supporting customers to generate, exchange, and report fully compliant e-invoices through the RTC Suite platform.
Getting ready for UAE e-Invoicing
The UAE e-invoicing mandate is one of the most significant changes since VAT was introduced in 2018. The UAE’s transition to e-invoicing is also aligned with global ‘VAT in the Digital Age’ initiatives, which aim to modernise tax reporting and enhance real-time transaction visibility. With pilot activities beginning in July 2026 and mandatory phases from 2027, businesses now have a clear but limited window to prepare.
In practical terms, preparation should focus on:
- Assessing your current invoicing flows and data quality,
- Selecting and onboarding an accredited ASP
- Mapping your ERP data to PINT AE and handling all relevant use cases,
- Testing end-to-end flows well before your go-live date.